Navigating the world of student loans can be a daunting task, especially with the myriad of loan options and repayment plans available. Understanding the nuances of each student loan program, including federal student loans, private student loans, and their respective interest rates, is crucial for making informed borrowing decisions. This comprehensive guide will delve into the various student loan options, exploring the advantages and disadvantages of each to help you choose the best fit for your financial circumstances. We will cover crucial topics such as loan forgiveness programs, income-driven repayment plans, and strategies for effectively managing your student loan debt. Whether you are a prospective student considering your funding options or a graduate grappling with repayment, this article will provide valuable insights into the complexities of student loan borrowing and repayment.
From understanding the difference between subsidized and unsubsidized loans to exploring the intricacies of loan consolidation and deferment, this resource offers a comprehensive overview of the student loan landscape. We will equip you with the knowledge necessary to navigate the repayment process with confidence, providing practical advice on budgeting, loan management, and avoiding loan default. By understanding your student loan options and repayment strategies, you can minimize financial stress and pave the way for a secure financial future. This article aims to empower you to make informed decisions regarding your student loans and successfully manage your repayment obligations.
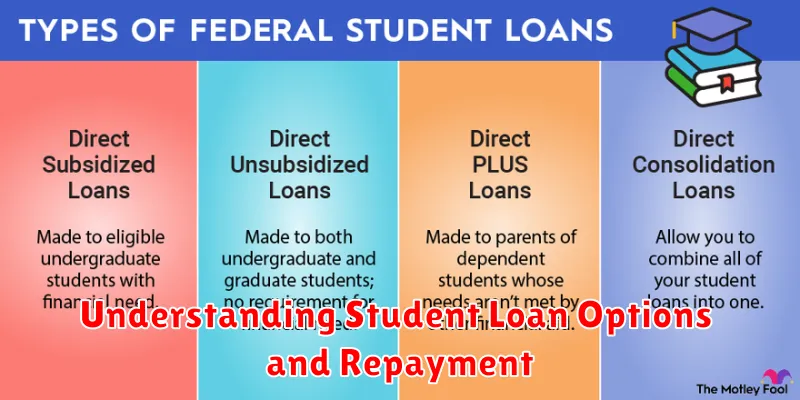
Types of Student Loans
Students seeking financial aid for higher education often encounter various loan options. Understanding the differences between these loan types is crucial for making informed borrowing decisions.
Broadly, student loans fall into two main categories: federal loans and private loans.
Federal Student Loans
Federal loans are funded by the government and generally offer more favorable terms, such as fixed interest rates and income-driven repayment plans. Common types include Direct Subsidized Loans, Direct Unsubsidized Loans, and PLUS Loans (for parents and graduate students).
Private Student Loans
Private loans are offered by banks and other private lenders. These loans typically have variable interest rates and fewer repayment options compared to federal loans. Eligibility and interest rates are heavily influenced by your credit score.
Federal vs. Private Loans
Choosing between federal and private student loans is a crucial step in funding your education. Understanding the key differences can significantly impact your repayment journey.
Federal loans are funded by the government and offer several benefits, including fixed interest rates, income-driven repayment plans, and potential loan forgiveness programs. Eligibility is primarily based on financial need.
Private loans, on the other hand, are offered by banks and credit unions. Interest rates can be fixed or variable and are often influenced by your credit score. Private loans typically require a co-signer, especially for students with limited credit history.
| Feature | Federal Loans | Private Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Lender | US Department of Education | Banks, Credit Unions |
| Interest Rates | Fixed | Fixed or Variable |
| Credit Check | Generally not required | Required |
| Repayment Plans | Income-driven options available | Limited options |
Understanding Interest and Grace Periods

Interest is the cost of borrowing money. It’s calculated as a percentage of the principal balance and accrues over time. Understanding how interest works is crucial for managing your student loan debt. There are two main types of interest: subsidized and unsubsidized. With subsidized loans, the government pays the interest while you’re in school at least half-time, during your grace period, and during deferment periods. Unsubsidized loans accrue interest from the moment they are disbursed, even while you’re in school.
A grace period is the time you have after leaving school before you’re required to begin making payments on your student loans. This period allows you to get financially settled before repayment begins. The length of the grace period varies depending on the type of loan. Federal Direct Subsidized and Unsubsidized Loans typically offer a six-month grace period, while some private loans may offer a different timeframe or none at all. It’s important to confirm the specifics of your loan’s grace period with your lender. During the grace period, you are not required to make payments, but interest may still accrue on unsubsidized loans.
Loan Repayment Plans

Choosing the right repayment plan is crucial for managing your student loan debt effectively. There are several options available, each designed to accommodate different financial situations and goals. Understanding these plans can help you minimize costs and avoid default.
Standard Repayment Plans involve fixed monthly payments over a set period, typically 10 years. This results in the lowest overall interest paid but may have higher monthly payments.
Graduated Repayment Plans offer lower initial payments that gradually increase over time, typically every two years. This can be helpful for borrowers anticipating increased income. However, it may result in paying more interest overall compared to the standard plan.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans base your monthly payments on a percentage of your discretionary income. These plans can be beneficial for borrowers with lower incomes, potentially leading to lower monthly payments. Some plans offer loan forgiveness after a certain number of years of qualifying payments.
Tips for Managing Debt Responsibly
Managing debt effectively is crucial for long-term financial health. This involves a combination of proactive strategies and mindful spending habits. By understanding your debt and creating a realistic plan, you can take control of your finances and work towards a debt-free future.
Create a Budget: Developing a detailed budget is the first step towards responsible debt management. Track your income and expenses to understand where your money is going. Identify areas where you can cut back on spending to free up funds for debt repayment.
Prioritize High-Interest Debts: Focus on paying down debts with the highest interest rates first. This approach minimizes the overall cost of borrowing and helps you become debt-free faster.
Explore Debt Consolidation: If you have multiple debts, consider consolidating them into a single loan with a lower interest rate. This simplifies repayment and can potentially reduce your monthly payments.
Make Timely Payments: Always make your debt payments on time. Late payments can negatively impact your credit score and result in additional fees.